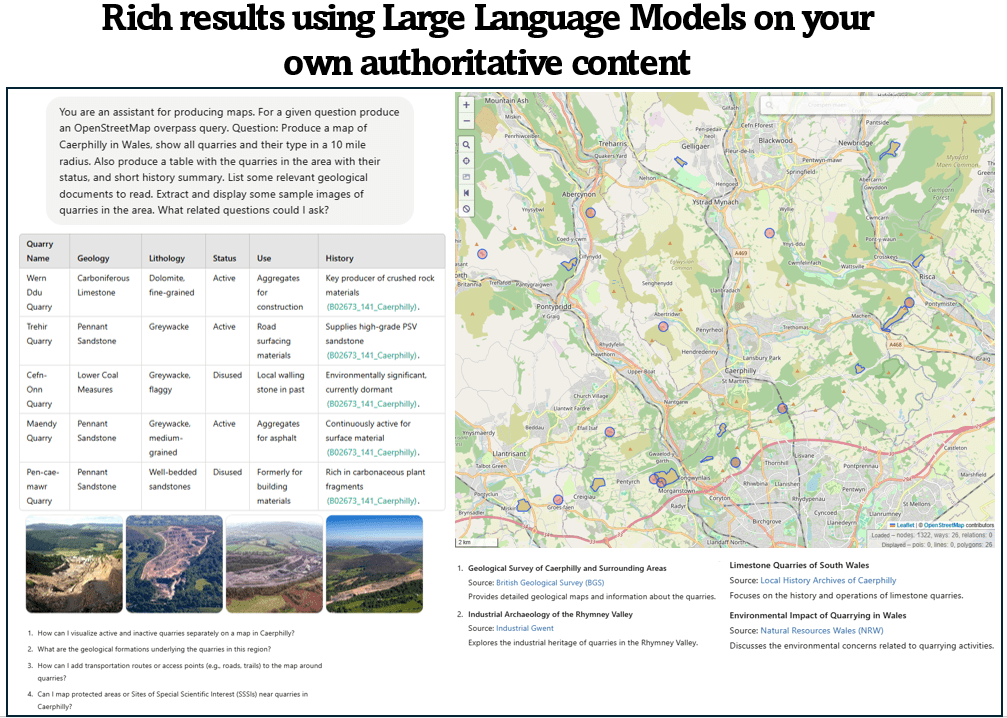
It can be relatively easy to create Large Language Model driven apps that exploit your own structured and unstructured data to produce rich results. This example is showing information on quarries in a certain area, combining data, text and geospatial information.
One difference in this approach between using Google search and ChatGPT type approaches, is that you can control results so they are derived from your own authoritative information and are referenceable back to the original source for transparency. A technique called Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG). To incorporate uncertainty within results, several different ‘sources’ can be utilised using the same query, to convey the sense of agreement or disagreement between answers.
In the toy example below I used GPT-4o prompt to illustrate. This can generate overpass queries to display in OpenStreetMap. This could be configured to generate an API query to another map system with your own spatial layers. The tabular data is generated from extraction of text from British Geological Survey PDF documentation (rather than Wikipedia for example). Follow up questions can be prompted in these rich multi-modal displays based on your own or authoritative content to stimulate a conversational experience.
This will not eliminate LLM “hallucinations”. However, by integrating results from numerous sources, using authoritative content and links back to the original source, may go some way to address the worst examples. I’ve included in the prompt a request to generate a list of more traditional search results lists to support the Gen AI content as this was a learning from a governmental projects with geoscientists.

Leave a comment