Measuring user satisfaction with an enterprise search tool can be difficult. Feedback mechanisms on the user interface tend to only capture a small self-selected sample that may be skewed towards negative views. Whilst surveys can capture more data, they are also self-selecting and tend to be small scale compared to actual enterprise usage. Clickthrough data is useful as a surrogate for search quality and session behaviour but does not necessarily translate into user satisfaction.
A small experiment was undertaken with a domain search tool in a large oil & gas company. Using the search log data, a random sample (n=47) of users who had used the search tool in the past 2 weeks were invited to participate in a questionnaire. They were asked to provide their level of satisfaction with the search tool based on the previous 2 week period using a 5 point Likert item. This was subsequently correlated with the existing search log data that they did not see (the number of days they had used the search tool during that 2 week period). Figure 1 shows the results.
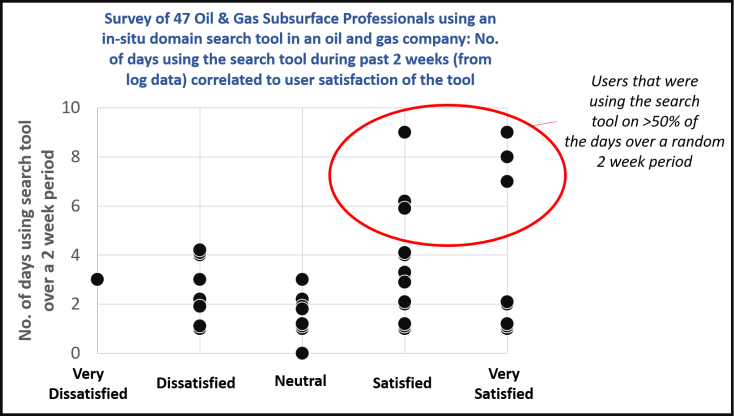 Figure 1 – Search satisfaction against usage (number of days during a 2 week period)
Figure 1 – Search satisfaction against usage (number of days during a 2 week period)
There were 6 users who were very satisfied but only used the search tool once/twice during the 2 week period. Conversely, there were six users who were dissatisfied that used the search tool only once/twice during the 2 week period. Gender and age was not statistically significant.
The data points outlined in the red circle are interesting. In the small sample tested, all the users who had used the search tool on over 50% of the working days (5 working days) over the prior 2 week period (10 working days), were satisfied/very satisfied. These could be considered ‘happy repeat customers’.
This could be a marker for inferring from large volumes of search log data, one subset of users who are satisfied with a search tool. This could be a marker for inferring from large volumes of search log data, one subset of users who are satisfied with a search tool. It is only a subset, as this group only represented 30.7% of all users who were satisfied (recall) but it was 100% accurate (precision).
As a causal mechanism, it is postulated that it would be unlikely that a user would use a search tool in an enterprise ‘every other day’ if they were not getting some value out of it. An alternative explanation is that the user has no choice, they have to use the tool as there is no other way to locate their information, i.e. high usage does not necessarily translate into satisfaction. However, there is plenty of evidence for poor take-up of enterprise search tools (people find other ways to locate what they need), so the best explanation is likely to be that they have some positive experience with the tool to explain the recurring behaviour.
That is not to say that users who use a search tool less are not satisfied of course (as these data show). This could be one marker for companies to assess user satisfaction exploiting large usage volumes rather than self selecting surveys. At present, there is no statistical significance to this finding and the data set is small, presenting an area for further research.

Nice work, Paul. Now that you have some ground truth search satisfaction data, it would be interesting to see if (given sufficient data) you could train a classifier to predict search satisfaction (perhaps on a per session basis) based on their real time behavior. That could enable all sorts of ‘in the moment’ support to uses based on their immediate needs, or perhaps post-hoc interventions based on their historical interactions.
LikeLike